Customer Service Digitalization Planning
Approach to planning of automation and technical initiatives for customer service.

Goals
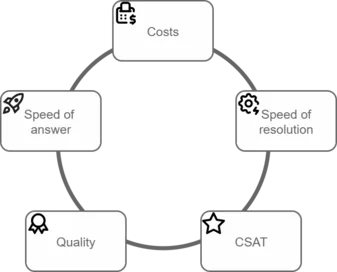
Any technical initiative for customer service aims at a limited range of goals:
Improving speed of answer: Making service more accessible by reducing wait times;
Improving speed of resolution: Making service quicker;
Improving quality of service: Better accuracy, consistency, and personalization of customer interactions;
Improving customer satisfaction: Creating positive experiences;
Making service cheaper: Cost savings are mostly associated with human resources costs and can be split into two areas: less work needed and less time spent per interaction.
Criteria
The potential for digitalization is massive, which is why it’s important to plan implementation strategically using these criteria:
- Strategy alignment with broader business objectives;
- Current level of digitalization vs. next desirable level — some projects build upon others;
- Tangible and mid-term relevant return on investment;
- Simultaneous development considerations: shared resources (people and systems) and overlapping targets.
Strategy alignment
Every digitalization initiative should directly support your organization’s strategic priorities. Ask yourself: Does this project advance our competitive position? Does it align with our customer experience vision? Will it support our growth targets or operational efficiency goals?
For example, if your strategy emphasizes premium customer experience, prioritize quality-enhancing tools over pure cost-cutting automation. If market expansion is the focus, invest in scalable solutions that can handle volume growth.
Current level
Digitalization follows a maturity curve. Understanding where you are today determines what’s feasible next:
- Level 1 - Manual: Paper-based or basic email systems.
- Level 2 - Digitized: CRM systems, ticketing platforms, knowledge bases.
- Level 3 - Connected: Omnichannel integration, API connections, data flow between systems.
- Level 4 - Automated: Chatbots, workflow automation, AI-assisted routing.
- Level 5 - Intelligent: Predictive analytics, autonomous resolution, continuous learning.
You can’t jump from Level 1 to Level 5. A chatbot won’t succeed without a solid knowledge base. AI recommendations require clean, integrated data. Assess your current state honestly and plan sequential steps.
Tangible and relevant return
Focus on initiatives that deliver measurable value within 12-18 months. Avoid vanity projects or purely experimental ventures unless you have dedicated innovation resources.
Calculate return across multiple dimensions: hard cost savings (reduced headcount needs, lower handling times), revenue impact (reduced churn, increased upsell), and risk mitigation (compliance improvements, reduced errors).
Ensure the return is relevant to decision-makers. A 5% improvement in CSAT might be more compelling to leadership than a 20% reduction in average handle time, depending on your organization’s priorities.
Overlap with other projects
Map all active and planned initiatives to identify dependencies and conflicts:
- Resource contention: Are multiple projects competing for the same developers, budget, or IT infrastructure?
- System dependencies: Does Project A need to complete before Project B can access required data?
- Target overlap: Are two initiatives trying to solve the same problem in different ways?
- Change fatigue: Will simultaneous rollouts overwhelm your customer service team?
Create a master timeline that sequences projects logically and maintains sustainable change velocity.
Example
Let’s consider a rapidly-developing mid-sized e-commerce company with B2C business model. The company strategically has two directions:
- Geographical expansion;
- 150% year-to-year growth on the customer base.
Level of digitalization:
- Out-of-the-box CRM solution (Zendesk, Freshdesk, etc.);
- Integrated web-form;
- CRM-embeded rudimentary macros;
- Basic knowledge base.
To support rapid company’s growth, service model should satisfy these criteria:
- Scalability (service budget should not grow proportionally to the customer base).
- Consistent quality.
- Best possible speed of service.
- Better understanding of the customer (VoC) to align strategy with the market needs.
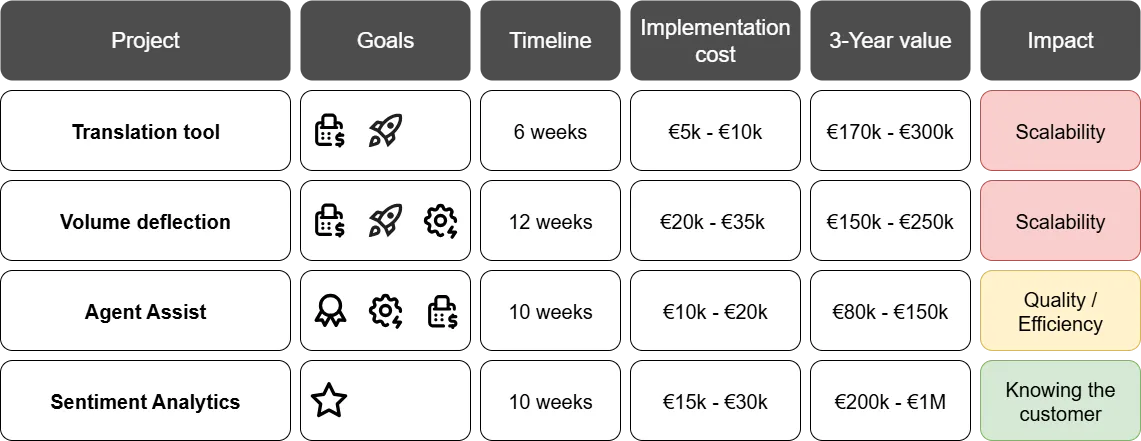
Following the business needs, those are potential digitalization initiatives for next 6-9 months:
- Translation tool Automatic (CRM-integrated) translation of customer interactions from EN to any language to support GEOX and limit costs on language-specific agents.
- Volume deflection Auto-response system to classify and answer most common queries, supporting economy on agents time and scalability
- Agent Assist Real time AI-assistant, providing agents with potential solution to received email, supporting efficiency and consistent quality.
- Sentiment Analytics Real-time sentiment monitoring based on support interactions that triggers automatic interventions and escalations.
Business case structure

Here is how to represent a digitalization project as a business case.
Problem statement
Clearly articulate the problem you’re solving with specific, quantified impacts.
Example:
Pain points: • 1550 emails/week require manual response; • ~ 20 % of volume – repetitive standard answer; • High risk of low SLA during seasonal peacks; • Resolution time 10% above target.
Cost of status quo: • € 60,000 annual cost of manual responses; • 7% payers churn during peack seasons.
Risks and mitigations
Be transparent about what could go wrong and how you’ll address it.
Common risks:
- Technology risk: System doesn’t perform as expected
- Mitigation: Proof of concept, phased rollout, vendor guarantees
- Adoption risk: Staff or customers don’t use the new solution
- Mitigation: Change management program, training, incentives
- Integration risk: New system doesn’t connect properly with existing tools
- Mitigation: Technical assessment, integration testing, fallback plans
- Scope creep risk: Project expands beyond original plan
- Mitigation: Formal change control process, steering committee oversight
Solution overview
Describe your proposed solution at the right level of detail for your audience. Focus on what it does and how it works, not just technical specifications.
Example:
What it does: “Email classification and auto-response system integrated with CRM that instantly respond to common queries with standard answer possibility.”
Features: • ML-based classification and text-analysis; • Pre-defined email answer templates; • Extended data (time-stamps) tracking tickets performance.
Integrations: • CRM: Freshdesk; • Knowledge base: email templates; • ML-powered plugin / or native solution; • API with SAP (later stages).
Resources required
Break down all resources needed for implementation and ongoing operations.
Implementation (one-time):
- Software licenses and setup fees: €XXX
- External consultants/integration partners: X days at €XXX
- Internal IT development: X hours at €XXX
- Training and change management: €XXX
- Testing and pilot programs: €XXX
Ongoing (annual):
- Subscription/maintenance fees: €XXX
- Support and monitoring: X FTE at €XXX
- Continuous improvement: X hours monthly at €XXX
Business impact
Quantify benefits across all relevant dimensions over a 3-year horizon.
Cost savings:
- Reduced contact volume to human agents: X tickets/month × €Y cost per ticket = €Z annually
- Lower average handle time: X minutes saved × Y tickets × €Z labor cost = €ABC annually
- Decreased training costs for new hires: $XYZ annually
Revenue impact:
- Reduced churn from improved satisfaction: X customers retained × €Y lifetime value = €Z
- Increased conversion from faster response: X% improvement × €Y revenue = €Z
Operational improvements:
- Agent productivity increase: X%
- First contact resolution improvement: X percentage points
- Customer effort score improvement: X points
Example:
ROI metrics: • ROI 120-150%; • Payback period: 4 months; • 3-Year value: € 210,000
Key benefits: • € 60,000 annual cost reduction (2026 budget); • Resolution time -8% reduction; • Extra 2.5 FTE flexibility for pick season.
Success metrics
Define how you’ll measure success with specific, trackable KPIs.
Example:
Success Metrics: • Deflection rate: 18%+; • Reopened tickets rate: 5%; • CSAT: maintain 3.9+ on auto-responses; • FCR : 8%+ improvement; • Cost per interaction: 12% decrease.
Roadmap
Provide a phased timeline that shows clear milestones and decision points.
Example:
Phase 1 - Foundation (Week 1-4):
- Analyze and identify symptom codes for automation
- Build first 20 templates
Phase 2 - Build (Week 5-7):
- CRM workflows configuration
- ML-model build
- Build deflection dashboard
- Sandbox user pre-testing
Phase 3 - Pilot (Week 8-12):
- Launch on NL only (single brand)
- Daily monitor over deflection vs tickets re-opening rate
- Build the rest of the templates
Phase 4 - Scale (Week 12-16):
- Full deployment across all countries / brands
Phase 5 - Optimize (Ongoing):
- Monthly performance reviews
- Launch templates maintenance and improvement methodology
Include decision gates: key points where you’ll evaluate results and decide whether to proceed, pivot, or stop.
Conclusion
Successful customer service digitalization requires balancing ambition with pragmatism. Start with a clear understanding of your strategic goals, assess your current capabilities honestly, and build a roadmap that delivers incremental value while working toward transformational change.
The business case framework outlined above ensures you can articulate not just what you want to build, but why it matters and how you’ll know it’s working. This structured approach increases stakeholder confidence, secures necessary resources, and sets your initiative up for measurable success.