Product Launch Support
Tactic to organize customer support for a new product launch and incubation.

Intro / Context
When a company launches a new product / service, customer service organization is expected to ensure operational readiness and seamless support integration.
Expected challenges:
- Customer inquiries volume increase (15-20%);
- Unstable or undercooked product;
- Knowledge gaps.
The organization of support operations is based on four pillars:
- Preparation: workforce, knowledge, systems;
- Support workflow setup;
- Knowledge & insights flow;
- Clear success metrics system and control.
Preparation
Flexibility beats perfection - you don’t need to be 100% ready but rather to have a flexible framework to adapt quickly to the changes
Workforce / Team
1. Expected volume evaluation
- Evaluate volume using historical data on similar products’ launches and sales projection
2. Capacity
- Calculate required FTEs based on the max. expected volume.
🔗 staffing calculator - Senior team members’ / team leads’ capacity for escalations and incubation tasks
3. Ramp-up planning
- Start with minimum staffing with next 3-6 months ramp-up plan.
- Keep hiring funnel ready for urgent ramp-up
4. Schedule
- Consider schedule changes based on the timezones coverage and geography of the launch
Knowledge
1. Train the trainer
- Team leads and / or senior team members are trained by product team.
2. Session with commercial team
- Learn the commercial value proposition and promises.
3. Training materials
- Prepare training materials, adapting the product and commercial knowledge to support aspects.
4. Team training
- Create digital self-study course.
- Organize live Q&A sessions.
5. Knowledge base
- Write initial articles, repeating training materials.
Systems
1. CRM system setup
- Add new product and category.
- Add new symptom codes.
- Setup new product view.
- Setup escalation queue (and views).
- Extra: templates and macros for later stages.
2. ERP system setup
- Create accesses for support team to new product related transactions, and order-to-cash process.
- Design operational views for support team.
3. BI system setup
- Create product support dashboard with CS metrics and flagging system.
Support workflow
New product launch should not eat all resources, attention, and SLAs, but rather integrate into standard support system as quick as possible
Inquiries routing
Here are some organizational principles to make new product integrated into existent support model:
- All support agents are capable of supporting new product. In most cases, dedicating a ‘pilot team’ or ‘product champions’ is unscalable solution that may cause a double work later.
- New product inquiries don’t have any extra prioritization in handling. Still company may have different SLAs targets per group of customers (e.g. VIP support, etc.), but new product cases handling should not be more important than others.
- Dedicated view (or queue) in CRM system for better visibility and control.
- Dedicated escalation queue to control knowledge gaps.
- Dedicated complaints / feedback queue (or view) for quick reaction on product improvement.
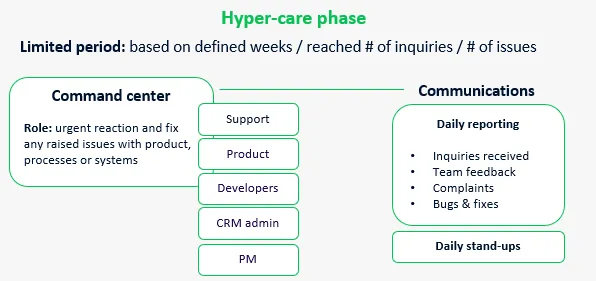
Hyper-care phase
- The goal of the hyper-care approach is a quick reaction and fixes of the issues related to product, processes and systems.
- For a defined period of time, special command center (also known as ‘war room’) supports internally all customer-facing departments.
- The key is organizing well-structured sequence of communications and information flow.
Risks
| Risk | Early signals | Mitigation tactic |
|---|---|---|
| Knowledge gap | AHT +20% CPC +50% QA -10pp | Uptraining; Daily / weekly Q&A sessions |
| Escalation overload | Escalation rate > 25% | Weekly product loop; KB content improvement |
| Unexpected product flaws | Complaints rate > 15% | Daily / weekly product feedback loop |
| Insufficient capacity / coverage | SLA -10 pp | Temp. staffing; Speedy ramping up; Reschedule |
| Too slow product adoption | Inquiries volume < 40% than forecast | Command center hibernation phase |
Knowledge & insights
Service team’s extra role is to continuously generate insights over the product, bugs, and improvements through customer interactions
Active phase
Period of preparation to the launch and active launching phase before support goes to the ‘business-as-usual’ stage.
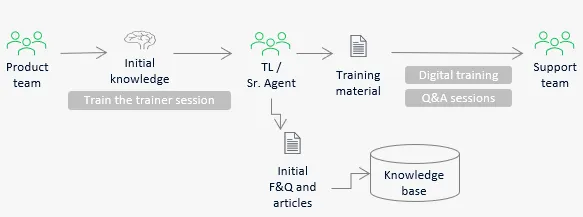
1. Initial knowledge flow
- Initial knowledge of the product is transferred to the support team (train the trainer) and then adapted to the service operations.
- Domain knowledge experts within the support team prepare training materials and train the rest of the team, including further uptrainings.
- Preferably, training should be in a digital format (self-study), but with live Q&A sessions.
- Besides training materials, product knowledge is formulated as articles in the well-organized knowledge base.
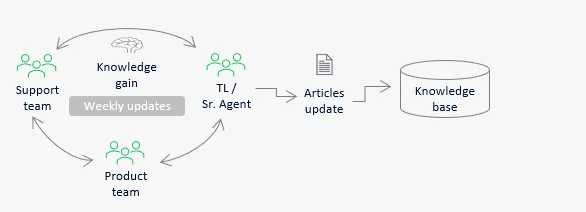
2. Knowledge improvement
- The purpose is to improve quality of product and support, avoid unnecessary escalations and speed up active launch phase.
- Support team generates insights (based on customer interactions) on product quality, issues and knowledge gaps.
- Daily / weekly update loop with product team helps with quick improvements and knowledge base updates.
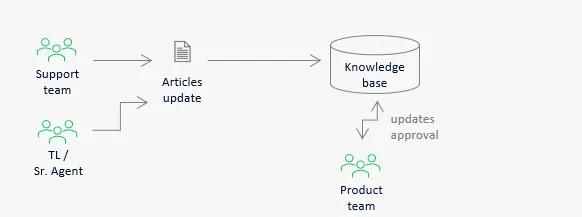
Maintenance phase
‘Business-as-usual’ phase requires standard process on continuous knowledge update and enhancement.
- Anyone can submit an update to the knowledge base, but it should be controlled and approved by the product (or support process) owners.
Success metrics
Maximum clarity on how you define successful launch from operational perspective.
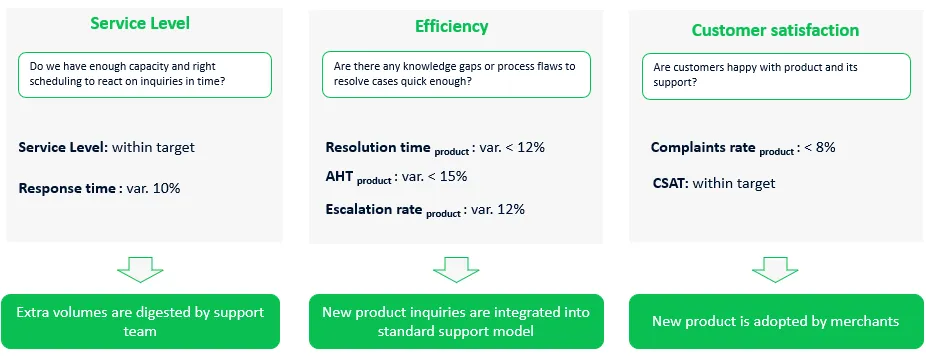
Service accessibility
Have we got enough capacity and right schedule to react to all customer inquiries in time?
- Service level (SLA): within standard target (e.g. 90% of emails are answered in 24 hours);
- Response time: can increase during the launch for not more than 10%.
By meeting service level metrics you can conclude that extra volumes generated by the new product are digested by support team.
Efficiency
Are there any knowledge gaps or process flaws that hurdle resolving cases quick enough?
- Resolution time new product : variance from entire portfolio metric within 12%;
- Average handle time (AHT) new product : variance from entire portfolio metric within 15%;
- Escalation rate new product : variance from entire portfolio metric within 12%;
- QA score: within standard company’s target.
By meeting the efficiency targets you can conclude that the new product inquiries are integrated into standard support model.
Customer satisfaction
Are customers happy with the new product’s support?
- Complaints rate new product : within 8% of all inquiries;
- CSAT: within standard company’s target.
By meeting the satisfaction targets, you can conclude that new product and its support model are adopted by customers.